목차
9. JOIN
- 내가 필요한 데이터들이 각각 다른 테이블에 분산되어 있을 때 데이터를 불러오기 위한 방법.
- Excel의 Vlookup 함수와 유사함.
- 서로 다른 테이블이 공통으로 가지고 있는 컬럼을 기준으로 묶게 됨.
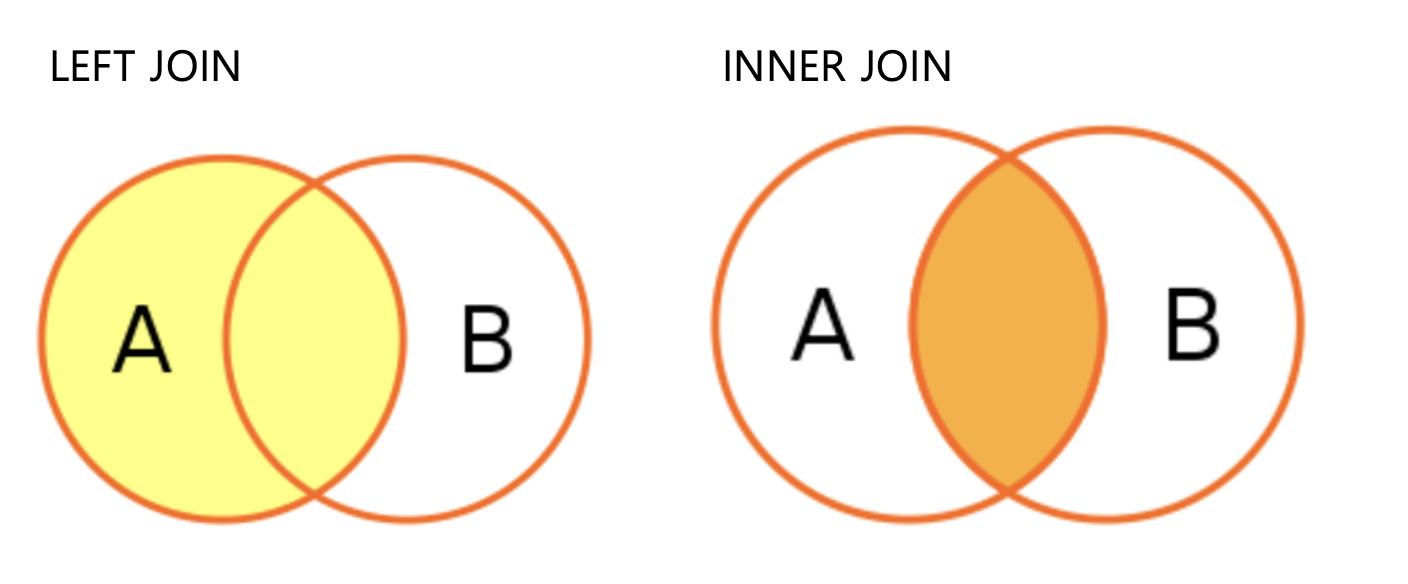
* LEFT JOIN
- 공통 컬럼을 기준으로 B 테이블에 값이 없더라도 모두 조회됨.
-- LEFT JOIN
select 조회 할 컬럼
from 테이블1 a left join 테이블2 b on a.공통컬럼명=b.공통컬럼명
예시)
SELECT *
FROM food_orders LEFT JOIN payments ON food_orders.order_id = payments.order_id
- LEFT JOIN은 없는 값도 조회되기 때문에 NULL값이 있는 것이다.
* INNER JOIN
- 공통 컬럼을 기준으로 두 테이블 모두에 있는 값만 조회됨.(NULL값 X)
-- INNER JOIN
select 조회 할 컬럼
from 테이블1 a inner join 테이블2 b on a.공통컬럼명=b.공통컬럼명
예시)
SELECT *
FROM food_orders INNER JOIN payments ON food_orders.order_id = payments.order_id
- INNER JOIN 은 공통으로 있는 값만 조회되므로 NULL값이 없음.
* RIGHT JOIN - 공통 컬럼을 기준으로 A 테이블에 값이 없더라도 모두 조회됨.

10. PIVOT TABLE
- 2개 이상의 기준으로 데이터를 집계할 때, 보기 쉽게 배열하여 보여주는 것.

예시)
Q. 음식점별 시간별 주문건수 Pivot Table 뷰 만들기 (15~20시 사이, 20시 주문건수 기준 내림차순)
1. 음식점별, 시간별 주문건수 집계
select a.restaurant_name,
substring(b.time, 1, 2) hh,
count(1) cnt_order
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
where substring(b.time, 1, 2) between 15 and 20
group by 1, 2
2. Pivot View 구조 만들기
select restaurant_name,
max(if(hh='15', cnt_order, 0)) "15",
max(if(hh='16', cnt_order, 0)) "16",
max(if(hh='17', cnt_order, 0)) "17",
max(if(hh='18', cnt_order, 0)) "18",
max(if(hh='19', cnt_order, 0)) "19",
max(if(hh='20', cnt_order, 0)) "20"
from
(
select a.restaurant_name,
substring(b.time, 1, 2) hh,
count(1) cnt_order
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
where substring(b.time, 1, 2) between 15 and 20
group by 1, 2
) a
group by 1
order by 7 desc- Pivot을 깔끔하게 만들기 위해서는 MAX를 사용해야한다.

11. Window Function
window_function(argument) over (partition by 그룹 기준 컬럼 order by 정렬 기준)- window_function : 기능명 사용. (sum, avg 와 같이 기능명이 있습니다)
- argument : 함수에 따라 작성하거나 생략.
- partition by : 그룹을 나누기 위한 기준. group by 절과 유사.
- order by : window function 을 적용할 때 정렬할 컬럼 기준 설정.
* RANK() OVER()
- 전체/ 특정 그룹 중 값의 순위 확인.
- ORDER BY 절 필수
- 순위를 구할 대상을 ORDER BY절에 명시.
- 그룹 내 순위를 구할 경우 PARTITION BY 절 사용.
SELECT RANK() OVER([PARTITION BY 컬럼] ORDER BY 컬럼 ASC|DESC)
예시)
1. 음식 타입별로 주문 건수가 가장 많은 상점 3개씩 조회하기
1) 음식 타입별, 음식점별 주문 건수 집계하기
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
count(1) cnt_order
FROM food_orders
GROUP BY 1, 2
2) Rank 함수 적용하기
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
cnt_order,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY cuisine_type ORDER BY cnt_order DESC) ranking
FROM
(
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
COUNT(1) cnt_order
FROM food_orders
GROUP BY 1, 2
) a
3) 3위까지 조회하고, 음식 타입별, 순위별로 정렬하기
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
cnt_order,
ranking
FROM
(
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
cnt_order,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY cuisine_type ORDER BY cnt_order DESC) ranking
FROM
(
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
COUNT(1) cnt_order
FROM food_orders
GROUP BY 1, 2
) a
) b
WHERE ranking<=3
* SUM() OVER()
- 전체 총 합, 그룹별 총 합 출력 가능.
SELECT SUM() OVER([PARTITION BY 컬럼] ORDER BY 컬럼 ASC|DESC)
예시)
음식 타입별, 음식점별 주문 건수 집계하기
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
cnt_order,
SUM(cnt_order) OVER(PARTITION BY cuisine_type) sum_cuisine,
#누적합 시에 순차적으로 내려온다는 의미로 ORDER BY를 사용
SUM(cnt_order) OVER(PARTITION BY cuisine_type ORDER BY cnt_order) cum_cuisine
FROM
(
SELECT cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
COUNT(1) cnt_order
FROM food_orders
GROUP BY 1, 2
)a
ORDER BY cuisine_type, cnt_order
12. 날짜 포맷
SELECT 컬럼명,
DATE(컬럼명)
FROM 테이블
예시)
SELECT date,
DATE(date) change_date
FROM payments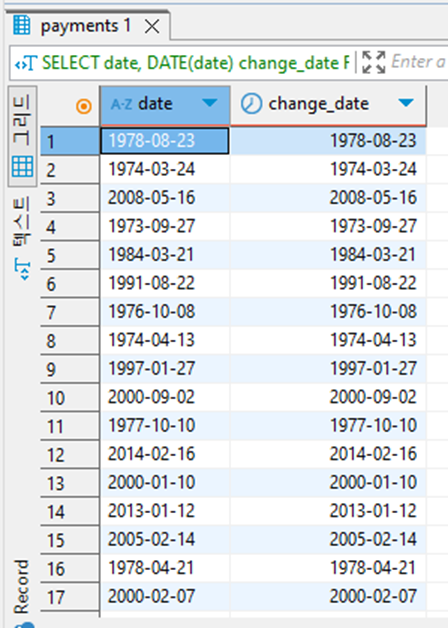
기존에 varchar 타입이었는데 change_date에서는 Date 타입으로 바뀌었음.
예시2)
select date(date) date_type,
date_format(date(date), '%Y') "년",
date_format(date(date), '%m') "월",
date_format(date(date), '%d') "일",
date_format(date(date), '%w') "요일"
from payments
- 년 : Y (4자리), y(2자리)
- 월 : M, m
- 일 : d, e
- 요일 : w (0은 일요일, 1은 월요일)
'스파르타 내일배움캠프 > TIL(Today I learned)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 25.02.18 TIL - 웹개발 미니 프로젝트(1) (4) | 2025.02.18 |
|---|---|
| 25.02.17 TIL - Git & Github (0) | 2025.02.17 |
| 25.02.14 사전캠프 TIL - SQL 조건문 (1) | 2025.02.14 |
| 25.02.13 사전캠프 TIL - SQL 기초 (0) | 2025.02.13 |
| 25.02.12 사전캠프 TIL - Java의 실행과정 (1) | 2025.02.12 |



